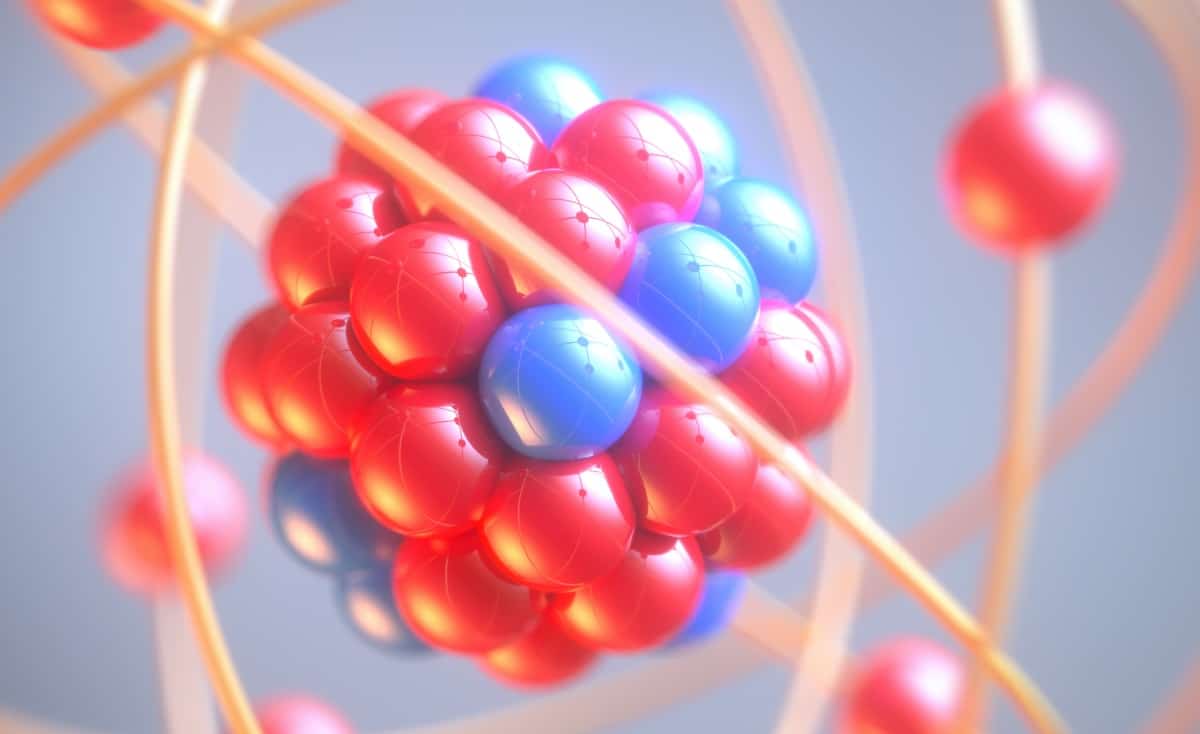
Isotope is a form of same element with atoms having the same atomic number but different atomic mass number, that is, the isotopes of an element will have the same number of protons but having different number of neutrons in their nucleus.
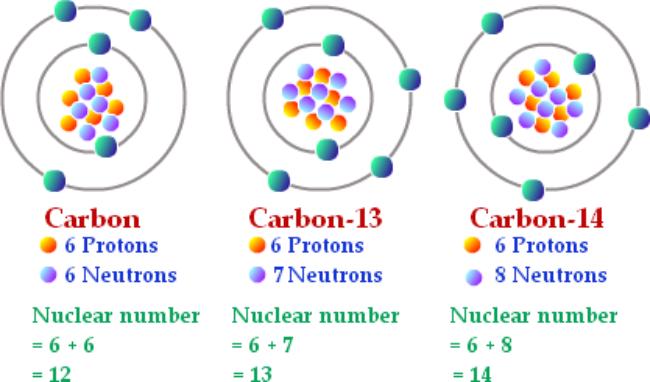
For example, there are three main isotopes of carbon. As the atomic number of a carbon atom is 6, each carbon atoms have 6 protons in the nucleus, but its isotopes can have either 6, 7, or 8 neutrons. Since the atomic mass numbers of these are 12, 13 and 14 respectively, the three isotopes of carbon are known as carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. Carbon in everyday life and in chemistry is a mixture of Carbon-12 (about 98.9%), Carbon-13 (about 1.1%) and about 1 atom per trillion of Carbon-14.
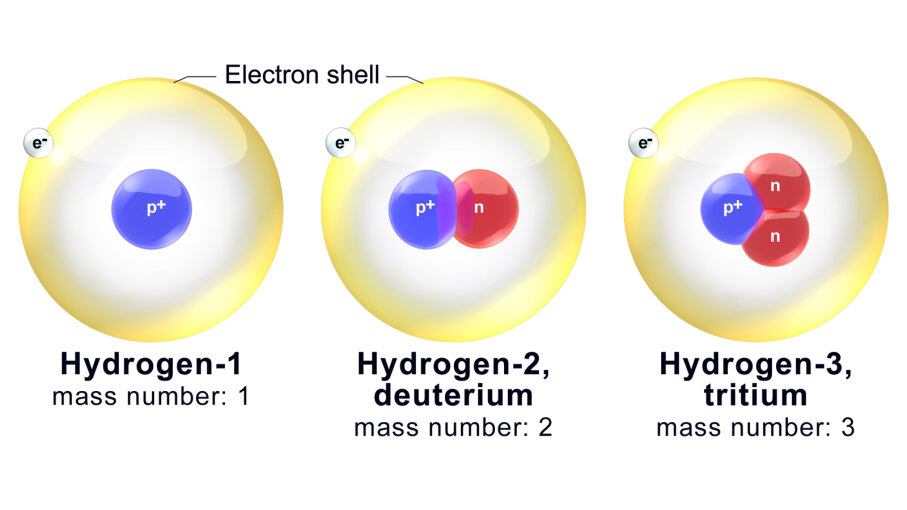
Most (66 of 94) naturally occurring elements have more than one stable isotope in which the isotopes of a given element are chemically nearly indistinguishable, except for the isotopes of hydrogen which differ greatly from each other in relative mass that enough to cause chemical effects.
Comments
Post a Comment