The s-block is on the left side of the periodic table and is composed of elements from the first two columns, the nonmetals hydrogen and helium and the alkali metals (in group 1) and alkaline earth metals (group 2). Their general valence configuration is ns¹⁻². Helium is an s-element, but nearly always finds its place to the far right in group 18, above the p-element neon. Each row of the table has two s-elements. Chemically, all s-elements except helium are highly reactive. The metals of the s-block from the second period onwards are mostly soft and have generally low melting and boiling points. Most impart color to a flame.
- Alkali Metals
Alkali metals are the chemical elements in the first group in the periodic table system. The alkali metals are lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Sodium is the most important alkali metal whereas Lithium is the least reactive. Although it was thought before that francium would be the most reactive, although it is very rare, it was more recently predicted that cesium is in fact more reactive than francium due to relativity.
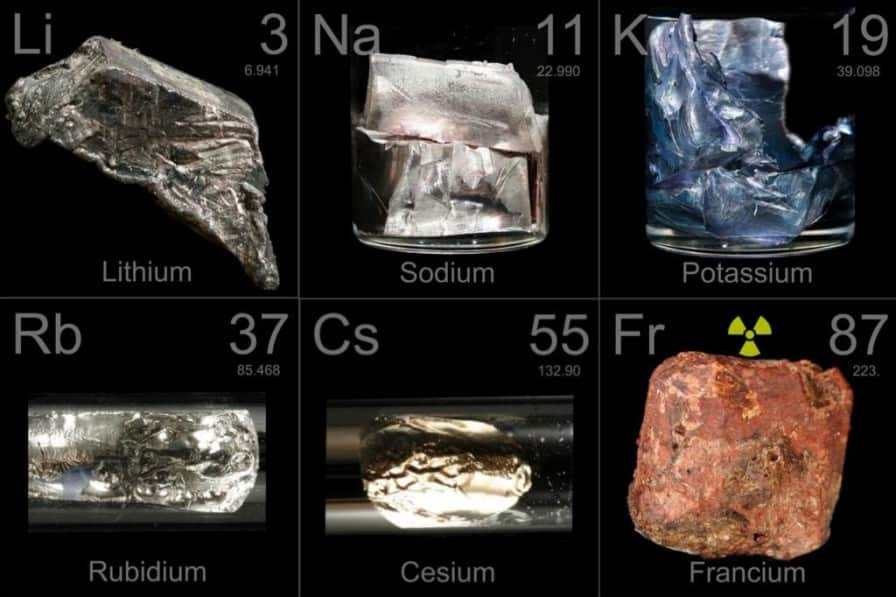

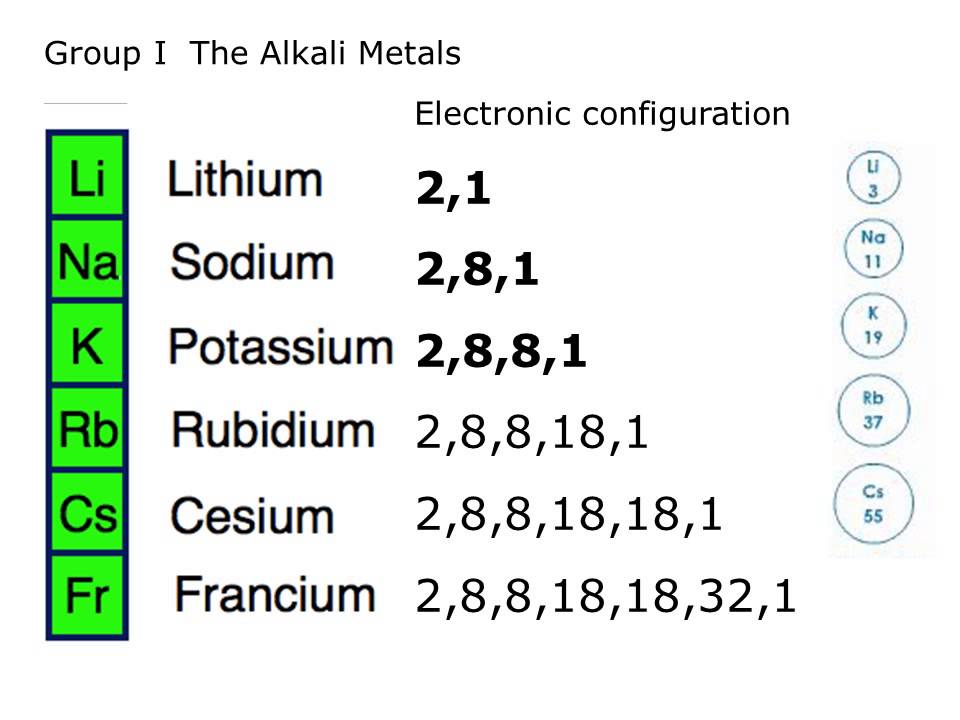
They are blood-colored when pure, hard and have only one valence electron. They including Hydrogen like to make reactions in which they give up this electron and then have a charge of +1. But Hydrogen is included in this group since it is a non-metal gas. They react strongly with water and because of this, they have to be stored in oil. They are never found in nature uncombined because they are unstable and they react fast to other elements. They bond well with all elements except the noble gases. When they are in air, they quickly turn black.
- Alkaline Earth Metals
The alkaline earth metals are the second group of metals on the periodic table. The alkaline earth metals are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). Radium is very radioactive.Structurally, they, including helium, have in common an outer s-orbital which is full; that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons. But Helium is a non-reactive and non-metallic, noble gases.

They are related to the Alkali metals, but they do not react as much because as ions they have a charge of +2 that they need more energy to remove their two electrons, so they do not have to be stored in oil. The alkaline earth metals are mostly shiny, silvery-white colored, soft metals, which react readily with halogens and water to form salts, though not as rapidly as some of the alkali metals, to form alkaline hydroxides.

Comments
Post a Comment